Digitalization and digital transformation are impossible without the use of IT systems. IT systems and digital technologies - tools for automation, digitalization and digital transformation .

And one of the key factors for successful implementation is setting the right tasks and goals before implementing the project. This is confirmed by international studies.

And to do this, it is necessary to understand why certain systems are created and what can be obtained from them. And this article will be devoted to an analysis of the main types of IT systems that you are most likely to encounter in life.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the classifier from the Ministry of Digital Development of Russia.
Content:
Now almost all vendors offer systems with hybrid functionality and various modules.
The reason is simple - companies want to implement one system that will have everything, and not have zoos of systems with crutches for pulling data. Whether this is right or not is another question. But nevertheless, we will highlight the main, most popular modules and figure out what it is, what it is for, and what it is used for.

During our research for the Tomsk region, we reviewed more than 100 practical cases on the implementation of digital systems (10 were included in the report). And the vast majority of projects that were called ERP are not such in their pure form. They include various modules (MES, MDM, WMS, etc.) and are hybrid.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) - enterprise RESOURCE planning system:
production capacity (volume planning - when and how many products should be manufactured);
human resources management;
process management and interaction between structural units (logistics, accounting, supply, production);
financial management;
asset Management.
ERP is primarily about money; in fact, these systems are aimed at financial and administrative accounting.
These systems are not suitable for operational planning of production, for example at the workshop level during the day. Firstly, they are about money and do not work with minutes, liters and pieces, and secondly, they are not intended for frequent plan adjustments and real-time data processing.
ERP is necessary for strategic/tactical planning and management, at the level of top management and managers/specialists of management departments.
For production management purposes, the use of these systems is advisable for weekly, monthly and quarterly planning.
Materials:
Links:
MES (manufacturing execution system) - production process management system.

If ERP is about money and medium/long-term goals (what is the profitability of the business, when it is necessary to update production), the headquarters and TOP need it, then MES is for PRODUCTION and tactical/operational management:
how to more efficiently utilize capacity and optimize processes under current conditions;
how many people are needed per shift;
how much we can produce per day, taking into account unplanned factors;
what is the cost of production;
in which area should a 24-hour shift be switched to, etc.
This system allows you to respond to changes before critical consequences occur and changes plans taking into account their impact.

Now this is one of the most popular types of systems for industrial enterprises. They are used in the context of a workshop structure, but they can be extended to an entire enterprise. The question is finances for the implementation and creation of productive infrastructure. Since there is a huge amount of production data (essentially a digital twin), and the processing time is much less than for ERP tasks and is of critical importance, these systems are extremely demanding on the performance of the IT infrastructure. And this is one of the main disadvantages of these systems.
And the second minus is that if you created the model (digital twin) incorrectly, then the cost of the error is fatal. You can simply ruin your equipment and lose control over production. There is definitely nothing good about this - checked.
Materials
Links:
Article on tadviser
Article on Tadviser: ERP is not difficult. The road to hell passes through MES.
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) is a product life cycle management system. “Classics” of product management systems.
PDM (Product Data Management) is a product data management system. It is distinguished by its large scale and wide functionality. In addition to the PDM, additional data is included.

These systems are designed to create a product immediately in digital form and support it throughout its life. It is most relevant for the industry of companies that create technologically complex products and want to improve the quality of their products, create new business models, immediately implementing full-cycle service contracts.
With their help:
you design a product and immediately understand what its performance properties will be;
identify errors in calculations at the design stage;
collect a retrospective (here the Internet of Things with an abundance of sensors can help);
predict the service life of the product and/or individual components, improve it based on the analysis of collected data (Big Data, Data science, artificial intelligence).
Now all the largest manufacturers design and manage their products in these systems:
auto (D aimler AG , BMW, KAMAZ and others);
air (B oeing , A irbus , Sukhoi, Lockheed Martin )
motor-;
shipbuilders and others.
The disadvantages include:
the final result still depends on people: they design and define the concept of both the product itself and what data needs to be collected;
The problem of all digital systems is the need for highly digital qualifications of employees. All industrial systems have complex interfaces and are not intuitive.
As a result, you need more qualified and expensive personnel, who are good engineers, and at the same time “advanced” in digital technologies and data analytics. And in order to manage such personnel, it is necessary to understand how motivation works, otherwise there will be large investments and minimal results.


Useful materials:
Links:
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a system for organizing interaction with customers.
The work of this system is based on the theory that the center of the entire business philosophy is the client.

It automates all stages of working with clients: from an advertising campaign and first contact with a potential customer, to after-sales support and warranty service, and the operation of a loyalty program.
When using this type of system, we get the opportunity to analyze all information about clients, communications carried out, amounts, deadlines, claims, etc.
Essentially, this is everything that sales managers used to do in Excel, only in a centralized and standardized system, where it is impossible to drag away the entire customer base and integration with other systems is possible.
For small businesses this is a must have. Especially considering that there are now a number of free products that allow you to try and evaluate their benefits. Thanks to this experience, the subsequent implementation of numbers will be more conscious and understandable for the company.
In essence, this system completes the formation of a comprehensive information “ring” of the organization.

Materials
Useful links:
SCADA (English: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) - supervisory control and real-time data collection about the monitored object, followed by archiving and preparation of a retrospective report and analysis.
The main tasks that SCADA solves:
process visualization (HMI);
operational control of the technological process;
alarm and event management;
analysis of historical data (trends);
generation of reports.
In essence, this is a system at the lowest, “technical” level in the hierarchy of the enterprise’s information environment. It employs operators and dispatchers. These systems are used where it is required to provide operator control over technological processes in real time with continuous, structured and automated data collection.
For maximum benefit, SCADA should serve both for dispatching complex production and systems (with subsequent search for bottlenecks), and as a source of data for enterprise IT solutions at a higher level (ERP, MES, APC, EAM)
More details about SCADA:
EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) - systems for optimal management of physical assets and their operating modes, risks and costs throughout their entire life cycle to achieve and implement the organization's strategic plans.
Simply put, these are systems for managing your equipment with maximum efficiency.
They help with:
financial management;
procurement management - it is possible to integrate with procurement management systems, it is possible to automatically register the receipt of components and parts at the warehouse, control delivery orders;
human resources management (HRMS);
asset management - a complete description of assets, technical. maintenance and repairs (requests for maintenance and repair, scheduling and estimates for work).
Those. will allow:
build a technical policy. maintenance and repairs (some are planned and some are condition-based repairs);
digitize and make transparent the entire MRO planning process: planning and carrying out work (create standard templates, avoid the human factor), attracting employees, necessary competencies, purchasing components;
consider the economics of an object or asset, make decisions and follow strategies (maximum reliability, maximum profit).


But these systems also have a number of global problems:
interfaces difficult to understand;
low digital literacy of the population;
high resistance to implementation for technical and cultural reasons (few people know how to work; few understand why; reluctance to change approaches and regret previously spent efforts; fear that staff optimization will begin, thanks to “effective” managers);
the risk of becoming a formal tool for accounting. reporting;
reluctance of non-core services (personnel, finance, planners) to immerse themselves. For them, this is a foreign system, but it needs their information to work correctly.
EAM systems in the information profile of an organization take over the circuit responsible for technical operation and reliability.
Materials
More information about EAM:
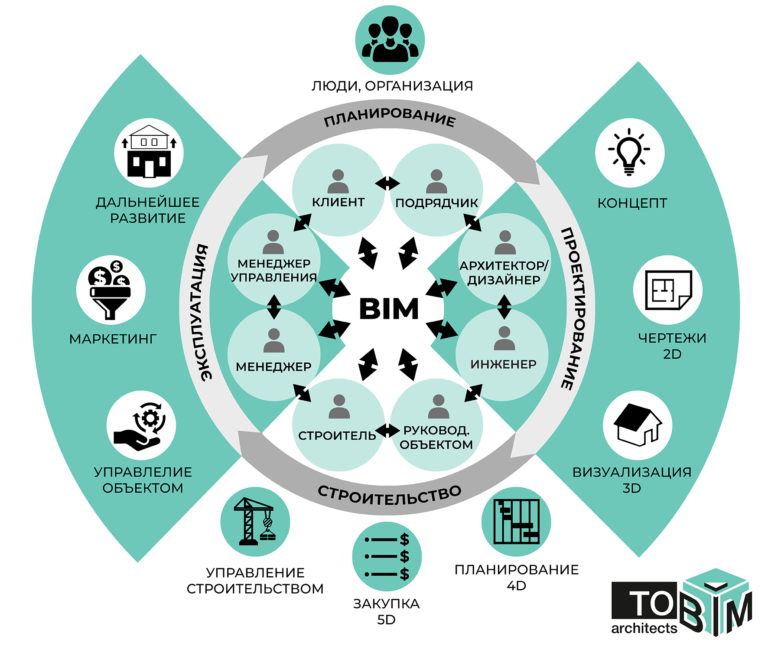
BIM ( Building Information Model or Modeling ) is an information model (or modeling) of buildings and structures, which in a broad sense refers to any infrastructure facilities, such as utility networks (water, gas, electrical, sewer, communication), roads, railways, bridges , ports and tunnels, etc.


Benefits of BIM
41% of surveyed companies noted a reduction in the number of errors after implementing the technology. 35% and 32% paid attention to improving communication between managers and designers and improving the image of the enterprise. Also a little more about the identified effects:
41% - reduction in errors
35% - improved communication between managers and designers
32% — improving the company’s image
31% - reduction in the number of design changes
23% - reduction in construction costs
21% — increased cost control and forecast accuracy
19% - reduction in time for project implementation
19% - entering new markets
A little about the benefits.
Objects in BIM are not just a 3D model, but information that can automatically create drawings, perform design analysis, etc., providing unlimited opportunities to make the best decision taking into account all available data.
BIM supports collaborative teams, so different specialists can use this information together throughout all stages of construction, which eliminates errors and loss of information during transfer.
BIM technologies allow you to accurately construct building engineering systems. Which reduces costs and the number of design errors.
Reducing the time spent on project development, as it becomes possible to implement some operations together.
A faster and simpler process of selecting the required equipment is carried out.
Accurate specifications and statements through automation.
The main economic and environmental characteristics of the building are determined already at the preliminary design stage, which allows changes to the project to be made in advance, if required.
It is possible to forecast estimates.
The construction process, management, control over the work schedule, and the consumption of materials and funds are being optimized.
Reducing maintenance costs and increasing equipment reliability throughout the facility’s life cycle
Disadvantages of BIM
BIM technologies are not suitable for the production of design documentation in Russia, resulting in the need to configure all parameters manually.
Quite a high cost of software ($6000-12000).
For effective operation of BIM technologies must extend to all areas of the facility, or rather to all sections. But this is not always the case with us. While many architects have switched to this format, adjacent sections are lagging behind . Therefore, the desired effect from information modeling does not occur.
High cost of training: programs are becoming more powerful, but at the same time more difficult to use. It takes a lot of time to learn.
There is a need to change the organization of the design process as a whole.
It is necessary to change not only the process and software, but also the psychology of designers, builders and operators.
Focus on architectural problems . BIM is good for solving problems of form formation, space use and design presentation, but it requires the use of other programs to carry out calculations.
Linking the process to a single software supplier.
Loss of existing work practices when moving to BIM.
Links:
We have already discussed various IT systems.
But the heart of any system is data or reference data - regulatory and reference information. Without them nothing will work.

At the same time, it very often happens that the data is there and the systems are working. But when working in them, for example, when choosing an object, you see 3-4 names that are the same or with minor differences (for example, LLC "Horns and Hooves", Limited Liability Company "Horns and Hooves" or Horns & Hooves). Or the same name at different levels.
The reason is “dirty” reference data systems.
Now imagine that you have several IT systems: ERP, MES, procurement, etc., which must “communicate” with each other, and you need end-to-end analytics?
There are 2 approaches to master data management:
1. Administrative - first clear out existing duplicates in IT systems, develop a coding system that can be used to compare entries in directories of different IT systems, and regulations. This method is relatively simple, but has a number of disadvantages - it will not prevent desynchronization of reference data in different systems, and regulations can always be circumvented.
2. Technological approach - implementation of an MDM system that ensures synchronization and a unified presentation of data.
MDM (Master Data Management) is a system for constantly identifying and managing the company’s master data (including master data): customers, products, services, personnel, technologies, materials, and so on.
You can also find another name - reference data management RDM (Reference Data Management).
MDMs manage:
collection;
accumulation;
cleaning;
comparison;
consolidation;
quality control and data dissemination within the organization;
ensuring consistency and control over the use of data across multiple operational and analytical applications.
As a result, MDM allows you to keep your data in order - to make sure that there is no duplicate, incomplete, or contradictory data in various areas of the organization.
There are 3 "large" types of systems:
1. Centralized.
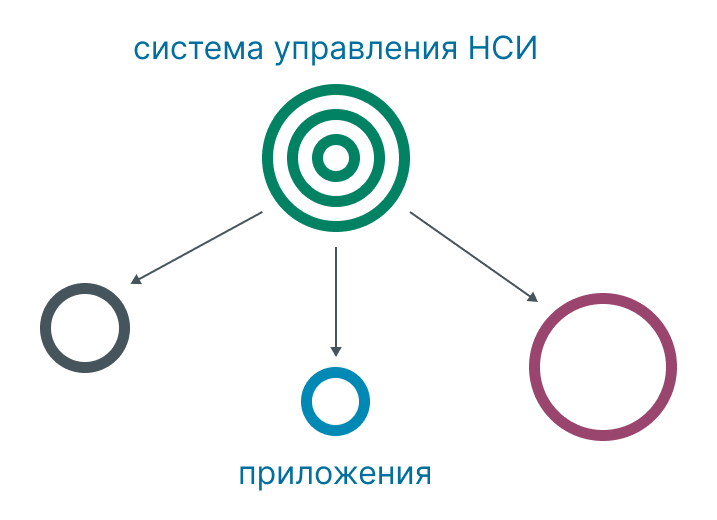
There is a “main” IT system. Reference data in this system will be considered standard, maintained in it and sent to other systems. At the same time, creating and editing reference data in other IT systems is prohibited.
Pros:
ease of implementation, maintaining the relevance and purity of reference data in all IT systems, administration and delimitation of rights;
current and clean reference data in all IT systems, which allows you to build clean local reporting in IT systems.
Minuses:
it is impossible to create and edit records defined in the central system through other systems;
The system is unstable to communication interruptions and its performance critically depends on the current availability of the central system.
2. Analytical.
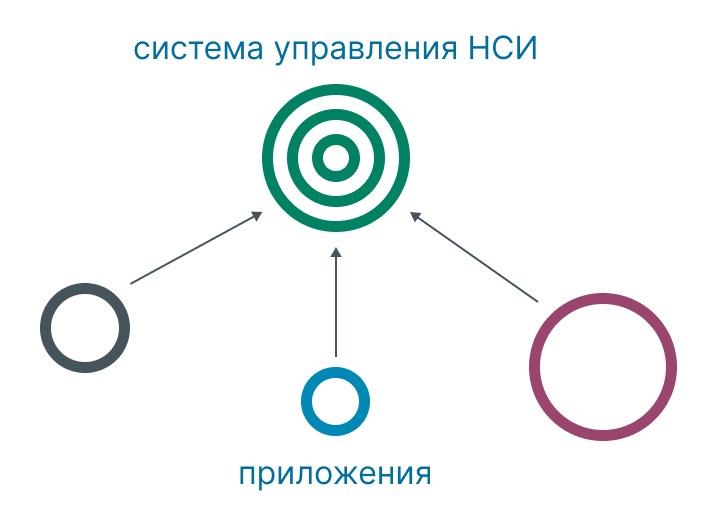
All master data elements are created in client systems, from where they are sent to the master data system, where a master data directory record is formed from these elements.
Pros: allows you to quickly implement the system, making minimal changes to client systems.
Disadvantages: there may be duplicates and reporting may be blurred, so building operational reporting is difficult (local reporting is also said to be “dirty” - local master data records may not correspond to records in the master data system).
3. Harmonized.
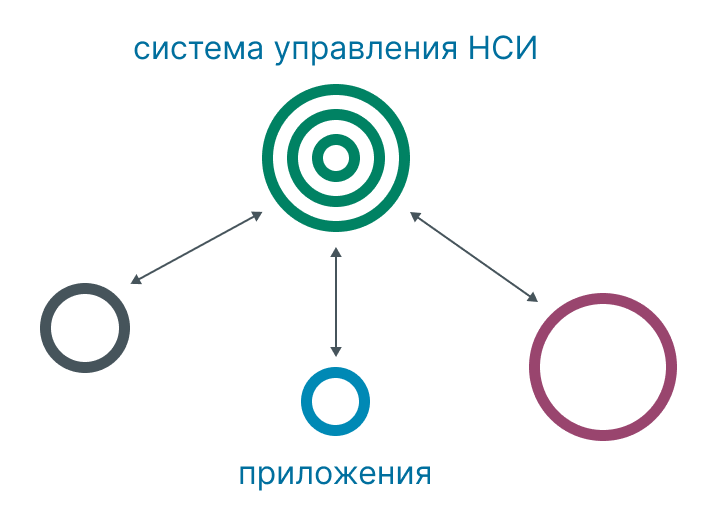
This system incorporates the best of centralized and analytical systems.
Pros:
allows you to enter data in IT systems, and then compare it with already entered data;
knows how to search for potential duplicates, resolve conflicts associated with simultaneous changes to the same data in different IT systems, and synchronize master data in IT systems. In this way, business processes are not changed or disrupted, and manual work on reporting preparation is minimized - that is, local reporting is simply built.
Disadvantages: these systems are the most expensive, labor-intensive and require serious expertise to build, and may also require modification of client applications.
Results:
Master data management facilitates:
implementation of new information systems in the company’s IT infrastructure;
integration of existing systems;
processing of corporate data;
reduces labor costs for updating data;
minimizes the risks associated with incorrect data.
The implementation of an MDM system is not always necessary or economically justified. But it is always worth remembering the problems that may arise due to desynchronization of reference data when developing the IT component of the company.
Links:
Materials:
WMS (Warehouse Management System), also known as WMS, is a system for automation and warehouse management.

When you see “addressed storage” or stories about automated warehouses with robots (for example, Amazon), they are based on exactly this kind of system.


The main goals for these systems are:
operational and tactical warehouse management;
increasing the speed of collection of goods;
obtaining accurate information about the location of goods in the warehouse;
effective management of goods with limited shelf life;
obtaining a tool to increase efficiency and develop processes for processing goods in the warehouse;
optimizing the use of warehouse space.
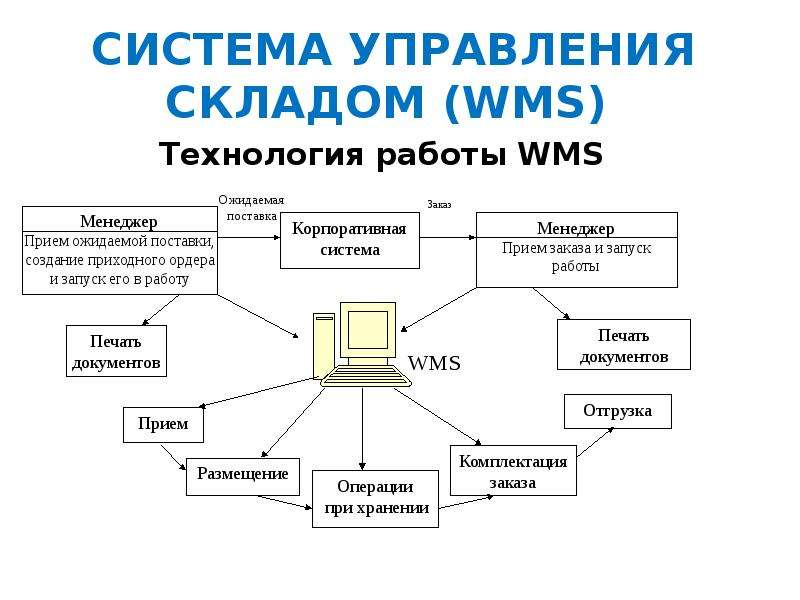
By size, WMS is divided into:
entry-level (warehouses of small companies, stores with a small product range);
boxed warehouse management systems (warehouses of 1000-10,000 m² with a large product range, but low turnover);
adaptable systems (large logistics companies, distribution centers, warehouses from 5000 m²);
configurable systems (warehouses from 5000 m² with a large product range and high turnover).
These are not the most popular and widespread systems, primarily used by logistics companies.
The feasibility of their implementation needs to be calculated.
More details about WMS:
SCM (Supply Chain Management) is a supply chain management system that automates the entire cycle: “supplier” - transport - production - storage - distribution - customers.”


SCM focuses on:
production;
supplies;
location;
stocks;
transportation + information.

Based on this, these systems solve the following problems:
Increasing the level of service;
Optimization of the production cycle;
Reducing warehouse inventories;
Increasing enterprise productivity;
Increased profitability;
Control of the production process.

As a result, SCM allows you to better meet the demand for the company's products and significantly reduce logistics and purchasing costs.
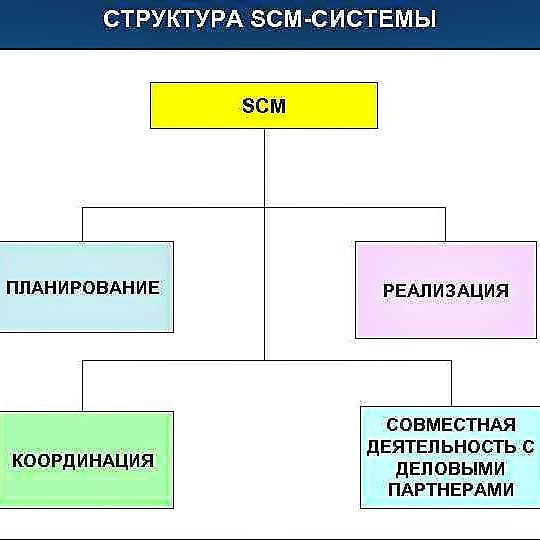
There are 2 blocks in SCM:
supply chain planning - planning and formation of schedules, decisions, design of supply networks, modeling of various situations, analysis of the level of operations;
supply chain execution - tracking and control of logistics operations.
Typical components of SCM systems:
product sales forecast (week and day);
inventory management - guarantee and current stock, taking into account the selected inventory management model for each product category;
replenishment management—planning deliveries within the company’s logistics network, taking into account planned sales, supplies of raw materials, availability of balances, transport capacities, various restrictions and business rules;
generating a report on necessary purchases, taking into account external restrictions (number of deliveries, minimum balance) and delivery schedules;
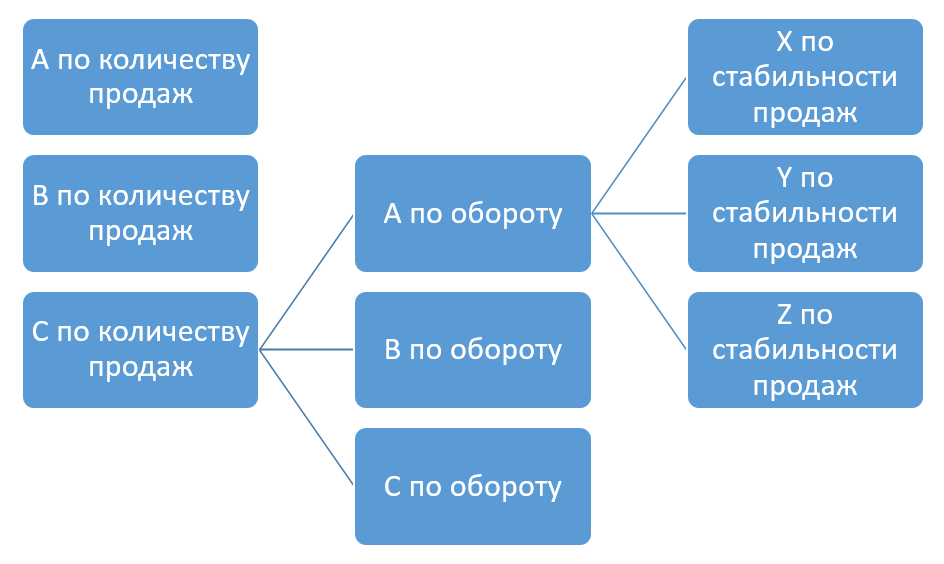
conducting ABC-XYZ and cross-ABC analyzes based on arbitrary criteria (quantity, profit, purchase cost);

visualization of sales, balances, prices, profits by goods and their groups;
taking into account arbitrary factors affecting sales in automatic mode;
calculation of the optimal stock for each item, taking into account the forecast of demand and safety stock.
These systems are used by the 10 largest IT companies, and the most effective is @apple , not much inferior to @dell , and @toyota is in the top 10
More information about SCM:
APS (Advanced Planning & Scheduling) is a system for production planning, with the ability to create a schedule for equipment operation throughout the entire enterprise.

Particular schedules in this system are formed taking into account the interrelations of all production stages when creating products.

Let's take a little look at the difference in production planning approaches between APS, MES and ERP:
- as we said earlier, ERP plans how many and what products should be released per month or quarter
- APS systems form certain initial work schedules of the first degree of approximation even before the start of the implementation of production plans. At the same time, due to the large dimension of the problem, many technological and organizational factors are not taken into account
- The MES system receives the scope of work, which is either presented by ERP at the stage of volume scheduling, or issued by the APS system in the form of a workshop work schedule acceptable for the enterprise, and in the future it not only creates more accurate schedules for equipment, but also monitors their implementation online. The goal of planning an MES system is not only to fulfill a given volume with the specified deadlines for completing certain orders, but to fulfill it as best as possible in terms of the economic indicators of the workshop. MES plans 1-10 shifts ahead.
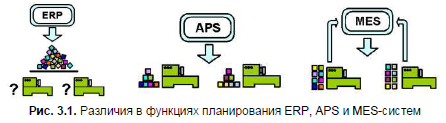
But again, all this is very conditional. Modern solutions are trying to cover an increasing number of “types of planning”.
As a rule, these systems include 2 modules:
1. Planning with business processes “as is”.
2. Modeling and calculation of the “optimization” effect.

Pros:
creating a “doable” and optimized plan;
support for working with plans (visualization of the plan, entering customer orders, viewing reports) via the web + restriction of functions and rights when working remotely.
Minuses:
Demanding requirements for the “maturity” of the company’s production system and its digital model: the availability and accuracy of the operational process and resources (people, machines, raw materials); organization of accurate and timely accounting (accuracy is no worse than “before the shift”);
Requirements for the hardware platform;
The need to have an “adult” planning system throughout the enterprise (including the supply of raw materials, personnel availability, etc.). Or will you have to do all this with 0, budget in this case...
Difficulty in support, especially if your enterprise is being restructured and processes, products, and BP relationships are changing.
Consequences of the minuses:
1. Inaccurate plan - people and equipment are standing still. Or the plan begins to shift to the right day after day.
2. With a large range of products and a weak hardware component, the system response time is long. This means your staff will swear and do everything manually. Receive huge resistance and sabotage. The result is either turnover and layoffs, or investments into emptiness.
3. Without a developed planning system... Think for yourself :)
In my opinion, despite the existence of independent solutions, this should be a component module of an ERP or MES system. Or better yet, a component of a complex enterprise IP.
This system will not solve problems (business processes, discrepancies between “paper” and life) in your enterprise, and will not bring order to chaos.
Useful materials
More information about APS:
BPM (business process management) is a business process management (BP) system with the ability to visualize both the BPs themselves and their relationships.
Answers the questions:
Where
When
For what
how and what work is done
who is responsible for its implementation.

Implementation goals:
Speed - reducing the time it takes to complete processes due to regulation, automation of steps and time limits for them;
Quality - due to the transparency of the business process for all participants, regulation and the availability of monitoring tools;
Data-driven management—sets of benchmarks (costs, execution time, and resource utilization) that facilitate process analysis and optimization;
Agility - achieving organizational flexibility by involving process participants in modeling and improvement.
Useful materials:
Links:
BI (Business Intelligence) - a system for generating reports and analytics.
The more source data (the more BP is digitized), the better analytics you can get.

Main features:
connection to sources from Excel to IT system databases;
building simple (graphs from tables) and complex reports, with end-to-end analytics from different systems;
fast creation of reports “on the fly”;
flexible configuration of access rights;
automation of preparation and distribution of necessary reports in various formats (Excel, HTML, PDF, etc.).
Problems to be solved:
Collection of data from different sources, their structuring and storage in a single system
Data analysis to form and confirm hypotheses, to develop business solutions taking into account analytics.
Modeling possible solutions to assess their impact on the bottom line and predict subsequent development based on available data.
Generation of operational and strategic reporting, including notification of deviations of indicators from acceptable standards.
Preservation and systematization of knowledge for the purpose of subsequent transfer to new employees, so that experience is preserved and the quality of work steadily improves.
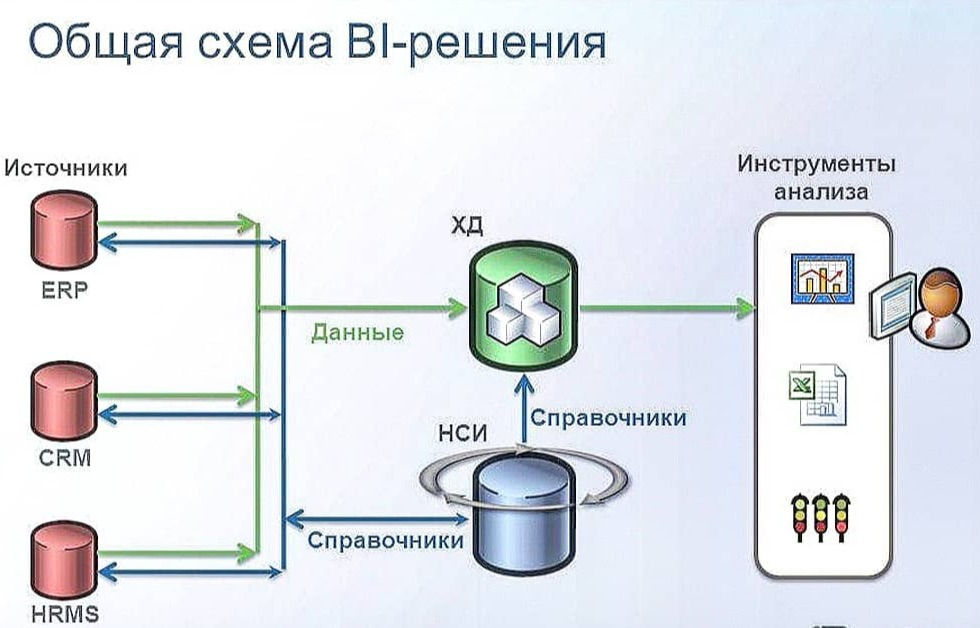
Perhaps the main disadvantage is the complexity of the interfaces, the need for special knowledge and training to work with these systems.
Links:
Materials:
Decision Support System (DSS ) is a system whose purpose is to help decision makers (DMs) in difficult conditions for a complete and objective analysis of subject activity. This means that it produces information based on input data that helps people quickly and accurately assess a situation and make decisions. DSS emerged from the merger of management information systems and database management systems .
In other words, DSS help to overcome and solve problems in:
Difficulty making decisions
The need for accurate evaluation of various alternatives
Necessities for predictive functionality
The need for multi-stream input (to make a decision you need conclusions based on data, expert judgment, known limitations, etc.)
DSS includes:
assistance to decision makers in analyzing the objective component, that is, in understanding and assessing the current situation and the restrictions imposed by the external environment;
identifying the preferences of the decision maker, that is, identifying and ranking priorities, taking into account uncertainty in the decision maker’s assessments and forming his preferences;
generation of possible solutions, that is, formation of a list of alternatives;
assessment of possible alternatives based on the preferences of the decision maker and restrictions imposed by the external environment;
analysis of the consequences of decisions made;
choosing the best option from the point of view of the decision maker.
DSS can be based on technologies/knowledge such as:
neural networks and machine learning
big data and end-to-end analytics, lakes and data warehouses
internet of things
cloud computing
digital twins
game theory, systems constraint theory
Now I want to give several approaches to classifying these systems.
1. Based on the data/model relationship (Stephen Alter’s method), DSS can be divided into:
FDS (File Drawer Systems - systems for providing access to the necessary data)
DAS (Data Analysis Systems - systems for fast data manipulation)
AIS (Analysis Information Systems - data access systems by type of solution required)
AFM(s) (Accounting & Financial models (systems) - systems for calculating financial consequences)
RM(s) (Representation models (systems) - simulation systems, AnyLogic as an example)
OM(s) (Optimization models (systems) - systems that solve optimization problems)
SM(s) (Suggestion models (systems) - systems for constructing logical conclusions based on rules)
2. By type of tools used:
Model Driven - based on classical models (linear models, inventory management models, transport, financial, etc.)
Data Driven - based on historical data
Communication Driven - systems based on group decision-making by experts (systems for facilitating the exchange of opinions and calculating average expert values)
Document Driven - essentially an indexed (often multidimensional) document store
Knowledge Driven - suddenly, based on knowledge. What does it have to do with knowledge, both expert and derived by a machine algorithm.
DSS requirements and attributes:
Quality
Organization
Restrictions
Model
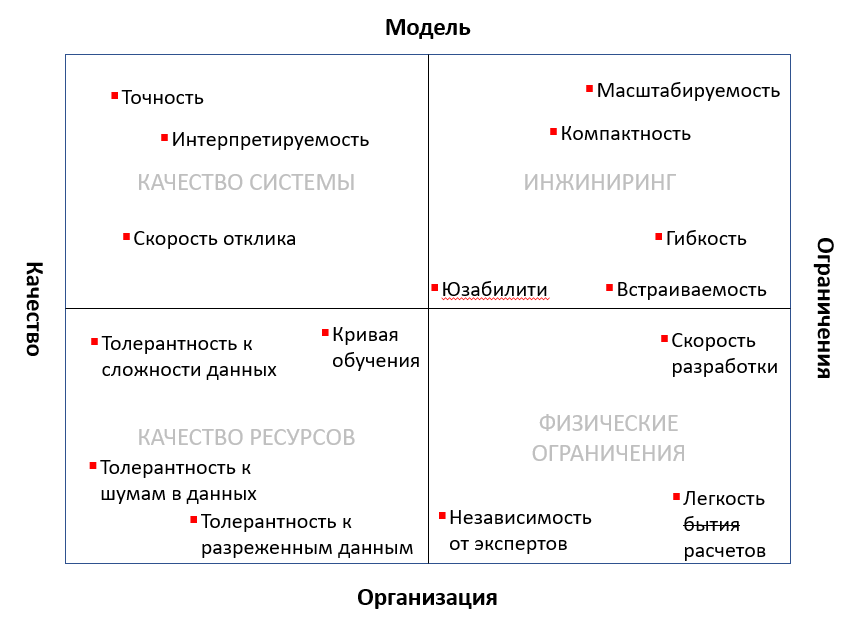
Below are 2 diagrams of the general organization of the DSS. They are identical, but emphasize different details.


DSS can be divided into 4 large layers:
Data collection (data warehouse, data lake)
Modeling
Data Mining
Interface

When building a DSS, you must adhere to the following steps:
1. Analysis of where and for what we will use DSS
2. Data collection
3. Data analysis
4. Selection of models
5. Expert analysis\interpretation of models
6. Implementation of models
7. DSS assessment
8. Implementation of ISDS
9. Collecting feedback. It is relevant at all stages
The disadvantages and limitations are identical to those of digital twins:
you need to be able to process data from different sources and with different structures, look for relationships in them (data science)
High-quality and labeled data needed
Must have strong math and management skills
be a critical thinker
be able to visualize, etc.
All this leads to the fact that these systems are still quite expensive and not possible everywhere.
Now, in 2021, the DSS is still in its infancy. While we are mastering BI systems - business intelligence systems. But they are the future. For example, Kamaz PJSC is already working on developing its own DSS . It will work based on Big Data analysis and will allow you to work with an order acceptance system, development time management, etc.
Links:
Videos and files:
PIM (Product Information Management) is a product management system that allows you to organize the process of filling out data by company departments and suppliers, taking into account customer questions and problems, as well as establish quality control of content/products/services.

PIM systems are aimed at:
Improving the quality and completeness of product information
More efficient creation of new products and management of their exports
Launching more product collections or ranges for promotional events and seasonal sales
Reduced time to market
Easier launch of new regions with relevant product information
Increase your team's productivity by automating tasks and streamlining workflows
To successfully implement PIM, companies need to correctly define and understand how they are going to use this system, what data is needed and for what decisions. That is, the question of the quality of the initiation and planning stages, and the development of data quality, again arises.
An example of data that can be included in a product description:
Basic data such as product ID, description, etc.
Hierarchy, that is, which category the product belongs to (and the categories may be different depending on the sales channel, for example, on your website there is one, on the marketplace another, etc.)
Technical specification, attributes such as diagonal for TV, color and size for shoes, etc. All this is aggravated by the fact that these attributes are different for different product categories.
Product-related files such as images, documentation, videos, etc.
Marketing data. These could be any tags, attributes for SEO, customer reviews, etc.
Information necessary for the sale, such as prices, delivery times, etc.
Sales channel-specific information, for example, categories on marketplaces, attributes specific to each marketplace, etc.
Localization, if sales are in different languages.
Manufacturing information such as certifications, allergens, composition, etc.
Logistics information: weight, dimensions with and without packaging, shelf life, etc.
Below are 2 examples: unstructured and structured product descriptions


And PIM systems have been developed to manage hundreds, thousands, and millions of these items. In manual mode this becomes impossible or very expensive.
Main stages of implementation:
1. Define the goals and scope of your PIM project
2. Define your team and processes
3. Determine your directory structure
4. Identify sources and collect data
5. Automate catalog management with business rules and bulk actions
6. Localize your products
7. Implementation of validation processes
8. Disseminate product information across sales channels
9. Collaborate, track progress and develop
Useful materials:
Links:
IDM ( Id entity Management ) is a system for managing access and user credentials.
Their goal is to improve the security and performance of information systems while reducing costs, optimizing downtime, and reducing repetitive tasks.
Initially, solutions of this class were focused on managing accounts in company information systems. Because systems were built incrementally, most organizations eventually developed heterogeneous environments where each information system handles account management differently. The task of IDM systems was to streamline and centralize the management and administration of accounts and automate the life cycle of accounts. Later, they added an access control function, and then IDM systems were transformed into IAM systems (Identity and Access Management).
While the abbreviations IDM/IAM prevail in the Russian market, the concept of IGA has already taken root in the international market. World analysts, for example, Gartner, use it in their research, assessments and forecasts.
Some of the benefits that IDM brings to an organization include:
A centralized source of information about employee accounts and access rights in information systems increases the transparency of access management;
Automation of account management based on personnel events reduces the number of errors and increases the level of information security;
The time spent waiting for employees to be granted the necessary rights is reduced due to a more transparent process for approving applications and making changes to IT systems.

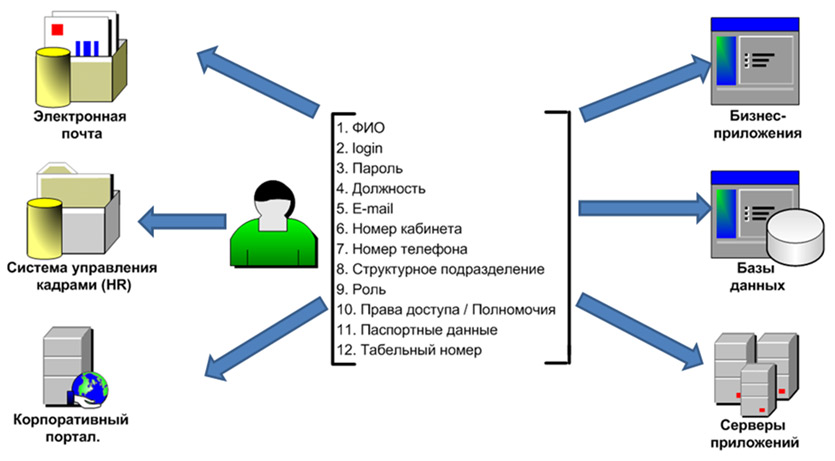
When planning implementation, it is necessary to conduct a survey/audit, prepare reference data and work out the issue of implementing the change
Among the limitations and disadvantages, I would note that many of these systems are not optimized and are not understandable for the end user.
Links:
Access management system (IDM): how to choose, implement and not be disappointed
Implementation of IdM. Part 1: what is IdM and what functionality applies to it
Implementation of IdM. Part 2. How to determine that it is worth thinking about implementing IdM?
Implementation of IdM. Part 3.2. How to build an access model?
Video:
DLP ( Data Loss Prevention ) is a system for preventing leaks of confidential information outside the corporate network. The system is built on the analysis of data flows outside the corporate network.

In recent years, DLP has begun to grow in depth, improving the quality of content analysis and interception. Thanks to this, data from DLP becomes invaluable for making any management decisions. This allows you to turn information security into a service for other departments of the company - from HR to economic security.
For example, modern solutions make it possible not only to respond to events, but also to prevent leaks by identifying employees with atypical behavior.
Links:
Video:
SRM (Supplier Relationship Management) is a system for managing relationships with suppliers. This class of solutions is used to optimize procurement.
These systems solve 3 problems:
supplier base management;
impact on suppliers;
supplier integration.
The database itself contains all the information about suppliers: addresses, contracts, amounts, and so on. And these systems automate the entire procurement cycle, from planning to closing the contract: coordination of procurement plans, selection of suppliers taking into account the chosen strategy, continuous control of supplies and budget expenditures. The goal of implementing these systems is to reduce procurement costs while maintaining quality and continuity of supply. In essence, this is a kind of variation of CRM and SCM
Useful links:
Electronic document management, which is a digital twin of the process , is the main project of any digitalization and digital transformation strategy.
Proper implementation of EDI helps speed up and simplify the transfer of various documents between individuals and legal entities. Sending and receiving electronic documents is much easier than paper ones. And most importantly, the process of their approval and signing is accelerated.
But if EDI is implemented within the framework of current processes, and there is simply a digitalization with minimization of manual work, then this is automation. A problem arises that some requirements are not canceled and losses still remain: it is necessary to wait for approvals for weeks and months, carry papers to the archive, etc. At the same time, even this implementation of EDI allows you to begin building process management.
The key task is to ensure that processes are optimized when implementing EDI, including eliminating unnecessary approvals. Then it’s digitalization and automation. It is also desirable that it be cloud-based.
At the same time, for attackers, EDI and SRM are the most desirable targets for attacks; they store confidential data about both the company and partners with all contracts. This information can either be sold to competitors or encrypted/deleted, which paralyzes the company's work.
Types of EDI
Internal EDI
Affects relationships between company employees. Internal EDI is poorly regulated by law, so each company may have its own rules.
Speeds up and simplifies the exchange of information within the company, including the communication of orders and other local regulations.
External EDI (with counterparties)
Most of the documents are standardized / templated. The routes for documents are also predetermined; you can configure the distribution of different types of documents among employees or departments.
This simplifies and speeds up interaction with counterparties and minimizes risks. However, if counterparties work with different EDF operators, it is necessary to enable roaming or agree on the use of a common system.
EDI with government agencies
EDI with government agencies, as a rule, involves submitting reports to regulatory authorities - the Federal Tax Service, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund, Rosstat, etc. For this purpose, there are special systems with up-to-date forms that make filling out reports faster and easier.
3 components of legally significant EDI (external and with government agencies)
EDF operator
Responsible for the accuracy of information about all participants in electronic document flow, records all actions occurring with the electronic document, and stores an archive of documents for the period established by law.
Electronic signature
Encryption of document contents and identification of who signed the document
EDI system
Automation of work with different types of documents and their storage
We looked at the main types of IT systems. But how to launch them?

The DH concept includes the use of cloud technologies, incl. through a Service as a Service approach.
This approach allows:
do not “freeze” finances with investments in fixed assets and future expenses (for repairs, renovations and modernization). This simplifies accounting and taxes, allows you to direct resources to development;
save on payroll (salary + taxes of expensive specialists for infrastructure maintenance) and operating costs (electricity, rent of premises, etc.);
save time on startup and use;
use computing power more efficiently. There is no need to build a “redundant” network to cover loads during peak times, or “suffer” from system “brakes” and risk a “crash” and loss of data. This is the task of the “provider”, and he will do it better, plus he will be responsible for it;
availability of information in the office, at home, and on business trips. This allows you to work better and more flexibly, and hire people from other regions.

There are many "types" of technologies: SaaS, IaaS, PaaS, CaaS, DRaaS, BaaS, DBaaS, MaaS, DaaS, STaaS, NaaS. Let's look at the most relevant ones:
SaaS (Software as a Service) - software as a Service
The most common in the world, used by almost all people with Internet access.
The client receives software products via the Internet. For example, mail services mail.ru. Gmail, or cloud version of 1C.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
Rent out computing resources in the form of virtual infrastructure: servers, storage systems, virtual switches and routers. Such an IT infrastructure is a full-fledged copy of the physical one.
PaaS (Platform as a Service).
Rent a full-fledged virtual platform, including various tools and services. The client can customize such a platform to suit his needs, turning it into a platform for software testing or, for example, a system for automating a control system. The service is especially popular among software developers

And a simplified visualization using the example of a pizzeria

Now this industry is developing and covers more and more areas of activity. The products being developed are becoming more and more hybrid and similar to modular platforms, in the heart of which is a database, and everything else is added on (example - 1C).
But almost all of them have one main drawback - a complex and inflexible interface . Almost no one applies lean manufacturing principles when designing them. Because of this, there are a lot of unnecessary movements and losses, and high labor costs for their support.
Also a big problem is the technical resistance of employees who do not understand what it is, why, how?
We recommend working through 2 directions:
1. Staff training.
There are also free courses, and we can help, both with training programs and support.
2. Initially try free services:
This approach will allow you to develop your own digital competencies, experience the benefits and approach the purchase of expensive systems more consciously.
Remember - IT systems will not correct crooked processes with poor management or a weak motivation system.
And all this should be for the sake of people, convenient for them, otherwise it’s a waste of money. UX|UI design must be optimized.
You also need to understand that it is necessary to build a comprehensive information environment for the enterprise. We implement either easily integrated products or modular platforms based on a data lake and BI .
If we consider specific recommendations for small and medium-sized businesses, we need to focus on:
CRM for digitizing the customer journey and its optimization, working with loyalty programs, automating typical scenarios, increasing the efficiency and productivity of the sales department. Here we recommend focusing on a combination of both classic tools (1C, Bitrix) and those that allow you to build loyalty programs (for example UDS )
PIM , if you have a large number of goods/products and distribution platforms to minimize the number of errors in product descriptions and simplify work with descriptions
ERP , if you already have more than 50-100 people and need to engage in full planning and accounting, tax reporting according to OSNO
DSS (digital advisors) that will allow you to focus on targeted work
And taking into account our experience in various digital projects, we realized that no implementation of IT systems is possible without project management, implementation of changes and high-quality communication, changes in business processes. As a result, we came to our own systematic approach , which is based on
Regular management practices
Implementing change: motivation, PR, resistance management and leadership
Strategy and metrics , organizational structure , business processes
All components are inextricably linked with each other. And the main key is communication management and a clear explanation of why.

We develop our own digital solution for your projects. You can get acquainted with it at the link: