Digitalization and lean manufacturing - a single whole?
- Джимшер Челидзе
- Apr 17, 2024
- 2 min read
The main goal of lean manufacturing is to eliminate all waste and activities that do not create value.
What is the meaning of digitalization?
First, you need to understand the difference between automation and digitalization, because these concepts are often confused.
Automation is the digitization and integration of IT technologies into existing processes. Its main advantage is the acceleration of existing processes. However, automation does not optimize them, and sometimes even duplicates them.
Digitalization is the introduction of information technology, accompanied by the restructuring of business processes, when work and decision-making are based on working with data.
While automation is limited to existing processes, digitalization transforms them by eliminating non-value-added activities.
Thus, the main task of implementing all IT solutions and digital transformation is to reduce the costs of obtaining and processing information, and therefore to reduce losses and inappropriate actions.
That is, the similarity between the goals of digitalization and lean manufacturing is obvious.
Moreover, digital technologies make it possible to better reveal the principles of lean manufacturing, and lean manufacturing allows you to create convenient digital services and increases the efficiency of digital implementation.
For example, you can additionally evaluate all IT initiatives and programs through assessing compliance with the principles of lean manufacturing, assessing what waste will be eliminated by the technology, whether lean manufacturing principles are applied when designing the UX design or system architecture of the digital solution / initiative.
Or, as part of the implementation of lean manufacturing and increasing operational efficiency, it is possible to conduct an additional assessment of which digital technologies can achieve greater effect.
Personally, in our practice of introducing digital solutions into clients’ business processes, we use the principles of lean manufacturing:
1. first we study the processes and customer journey;


2. then we identify places where the process brings maximum inconvenience to the user;
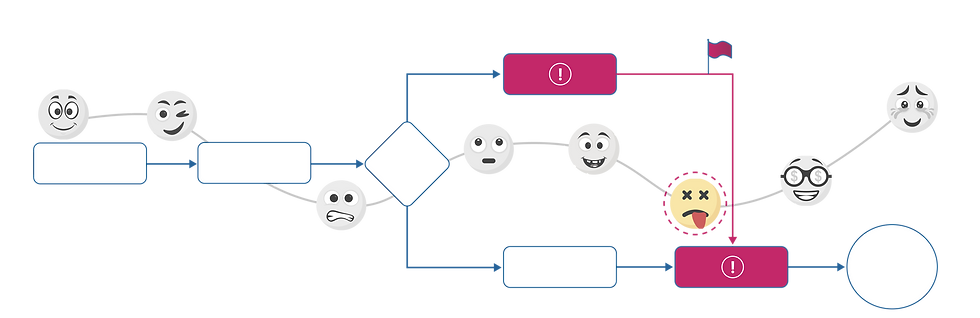
3. We evaluate the limitations of this process and find a digital solution;
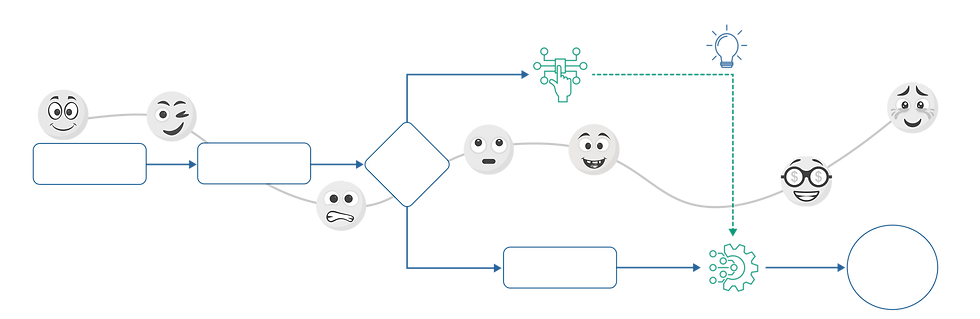
4. We are implementing a project for its implementation;

5. and while the client is happy with the results, we find a new limitation that requires a solution.

This is how the PDCA cycle works - plan, do, check and improve. After all, there are no ideal processes; there is always something that can be improved. And every improvement means additional profit for the client and elimination of losses in the process. At the same time, rebuilding everything at once is also not the best idea - you will be engaged in endless design and will face a high risk of failure. The larger the initiative, the more difficult it is to implement it, more about this in the post about project management , the implementation of any changes is also essentially a project, as well as in the infographics below.

As you can see, even here you cannot do without the philosophy of lean manufacturing.
The presentation material is available for download: